When a vein, artery and nerve all run together what is it called?The splenic vein is joined by the inferior mesenteric vein, which is joined by the superior mesenteric vein which forms the portal vein What is a splanchnic nerve? The proper way to identify veins, arteries and nerves are their positioning in relation to body structures For example, under the intercostal bone margin the acronym to remember is VAN, as the vein, artery and nerve will always be in the same order
Human Being Anatomy Blood Circulation Principal Veins And Arteries Image Visual Dictionary
Artery vein nerve slide
Artery vein nerve slide-Explore Mary Lou Markwell's board "Muscle, Vein, Artery, Nerve", followed by 226 people on See more ideas about muscle, arteries, anatomyMusculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median, ulnar nerves Lower extremity Arteries femoral, popliteal, anterior tibial, posterior tibial, dorsalis pedis arteries




Human Artery Vein Nerve Cross Section Prepared Microscope Slide Eisco Labs
The posterior intercostal artery travels in the costal groove between the intercostal vein and nerve The vessel first passes in the endothoracic fascia before passing between the internal and innermost intercostal muscles Do you want to Important veins of the leg include the internal and external iliac veins, femoral vein, saphenous vein, popliteal vein, tibial vein, and the venous arch of the foot Nerves in nerves are white arteries are round veins are flat lymph nodes tend to be kinda round, shiny, and dark ganglia look like lumps of fat plexi look like random debris on top of whatever the relation is, ie aortic plexus
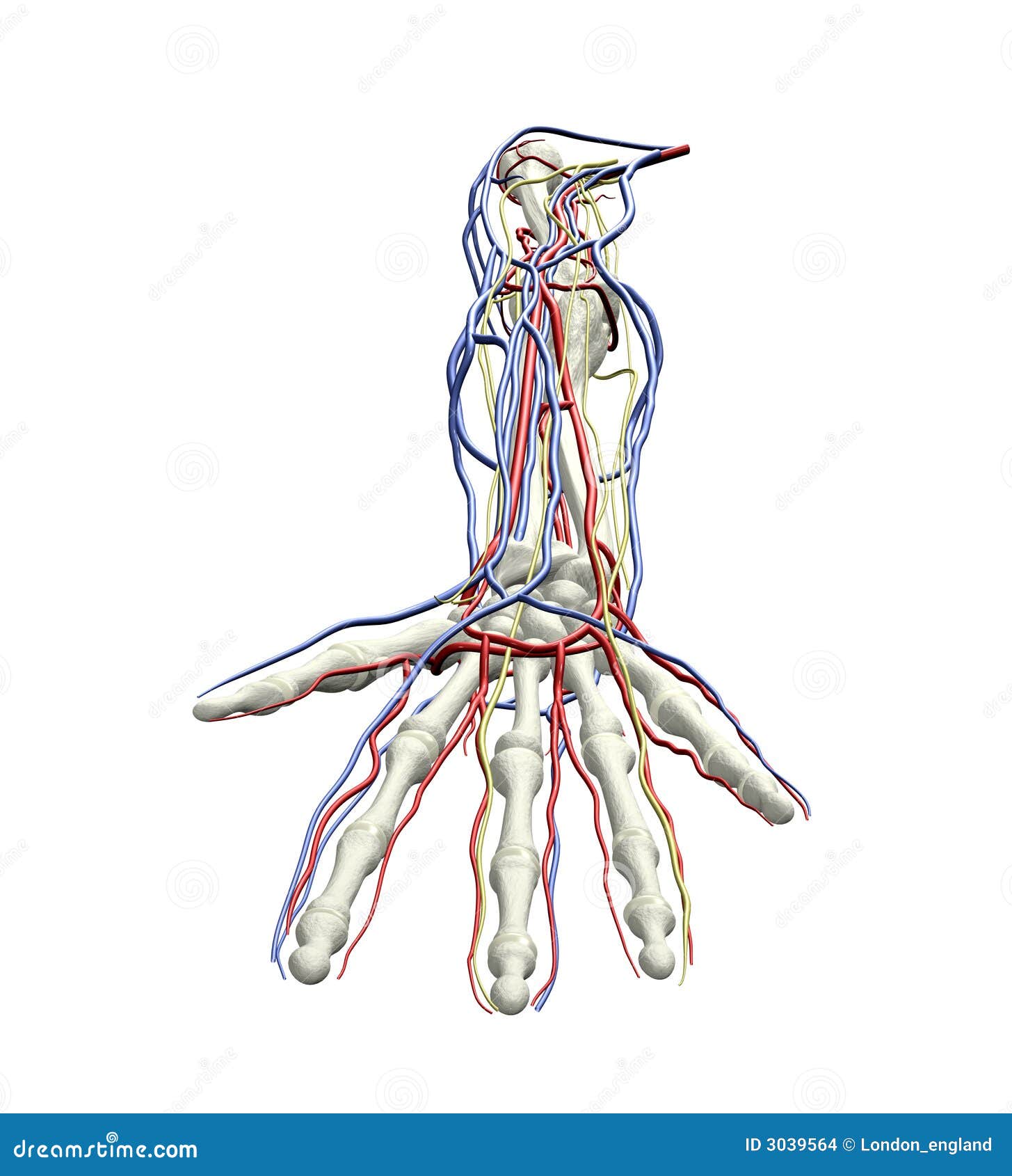
Nerves, Arteries, and Veins of the Wrist and Hand Busy muscles need plenty of nerve supply and blood flow Three main nerves (plus all their branches) work the wrist and hand, and many arteries and veins bring blood into and out of the hand The names of the deep veins are the same as the names of the artery they accompany There are two important superficial veins the great and lesser saphenous veins The great saphenous is often used in coronary bypass operations as it has thicker walls than most veins and therefore it can substitute for an arteryDifference between Nerve and Vein Key Difference Veins are large return vessels of the body which carry blood to the heart They can be considered as blood return counterparts of arteries Nerves are bundles of axons constituting the peripheral nervous system They transmit information between periphery and central nervous system
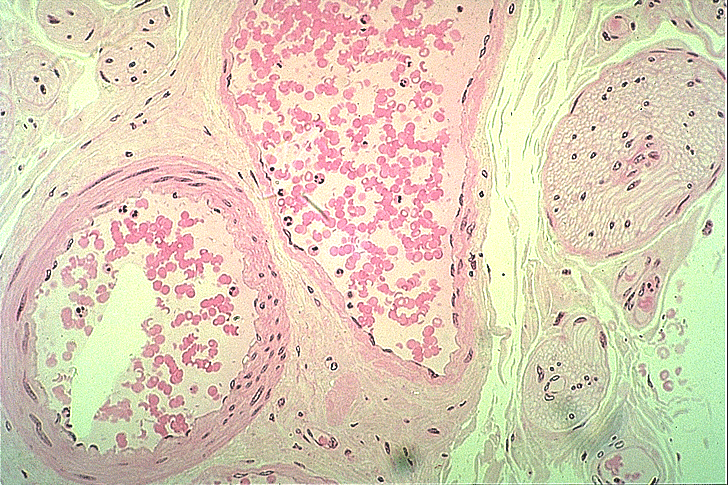
A compound set of veins and arteries preserve the heart and deliver blood to it; Start studying Artery, Vein & Nerve Histology Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsThe veins are originated in the cortex and follow parallel to the interlobular, arcuate, interlobar, and segmental arteries until forming the main renal vein Figure 1 The arcuate arteries (green arrow) run by the interstitial space between the cortex Similar to the arteries in the pelvis, veins branch within the legs As blood returns to the heart these branches — the external iliac veins — feed into the inferior vena cava , the large




Dorsal Hand Tendon Nerve Artery Vein Anatomy
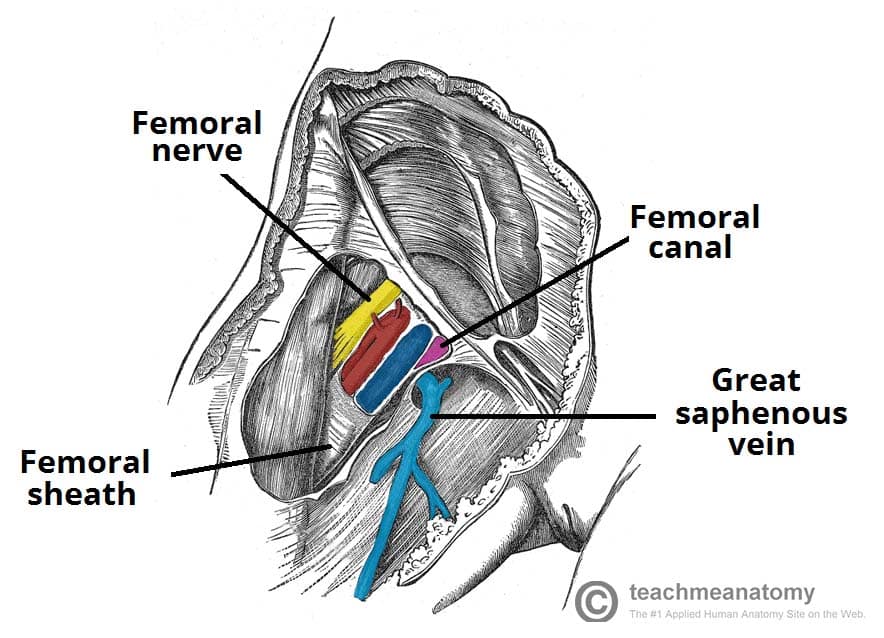



The Femoral Triangle Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy
Mnemonics NAVY From lateral to medial N femoral nerve A femoral artery V femoral vein Y "Yfronts" (ie the midline) It should be noted the mnemonic only pertains to the major structures and that the femoral triangle also Decalcification, staining the nerves, and decolorization and neutralization procedures were not carried out for 10 specimen sides with marked veins because the weak vein walls would rupture during the procedure of staining the nerves Therefore, examination of the arteries, veins, and nerves in a single specimen was not possibleAnatomy of the Nerves, Arteries and Veins of the Arm (Upper Extremity) Labels include cephalic vein, brachial artery/vein, basilic vein, musculoskeletal nerve, ulnar collateral artery, radial collateral artery, ulnar nerve/artery/vein, interosseous artery/vein, median nerve and radial nerve/artery/vein



Vasculitis Treatment Symptoms Causes And Types




Muscular Artery Vein And Nerve Bundles Surrounded By Adipose Tissue The Artery Is Identified As Having
Location The root of the right lung lies behind the superior vena cava and part of the right atrium, and below the azygos veinThat of the left lung passes beneath the aortic arch and in front of the descending aorta;Now up your study game with Learn modeMoreover, they permit the blood to flow from end to end of the organism We will write a custom Essay on Heart Fibers, Veins, Arteries, and Nerves specifically for you for only $1605 $11/page 812 certified writers online Learn More



1




Major Arteries Of The Body The Aorta Head Neck Torso
Structure The lingual artery first branches off from the external carotid artery It runs obliquely upward and medialward to the greater horns of the hyoid bone It then curves downward and forward, forming a loop which is crossed by the hypoglossal nerveIt then passes beneath the digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle running horizontally forward, beneath the hyoglossus The arteries, veins, and nerves that supply the kidney enter and exit at the renal hilum Renal Arteries The renal arteries branch off of the abdominal aorta and supply the kidneys with blood The arterial supply of the kidneys is variable from person to person, and there may be one or more renal arteries supplying each kidney Dorsalis pedis This artery supplies blood to the surface of the foot as a continuation of the anterior tibial artery It is accompanied by the dorsalis pedis vein The veins of




Obturator Nerve Artery And Vein Topographical Anatomy Open Surgery Right Download Scientific Diagram



Small Veins And Muscular Arteries
Superficial veins of lower limb Deep femoral artery has branches wrapping around the femur Veins accompany arteries Skin innervation Femoral nerve Obturator nerve Deep fibular nerve Superficial fibular nerve Anterior thigh and medial leg Medial thigh Area between the first two toes Anterolateral leg and dorsum of the foot Arm nervesArteries and veins lie in the nerve fiber layer and are separated from the inner limiting membrane (ILM) by a thin layer of neurons and glia Arteries are narrower and brighter red than veins Arterioles and venules then form two capillary networks in the deeper aspects of the retina a superficial network in the nerve fiber layer and ganglionThe correlation between the iliolumbar artery and the veins to the obturator nerve and the lumbosacral trunk was recorded Results The iliolumbar artery originated from the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery or from the internal iliac artery The mean diameter of the iliolumbar artery, at its origin, was 35±05 mm




Mammal Artery Vein And Nerve Simple Squamous Annotated 40x Histology



How To Tell The Difference Between An Artery Vein And Nerve From A Photo Quora
Peripheral Manifestations of Nerve, Artery, and Vein Disorders Confusion abounds among disorders of nerves, arteries, and veins because terminology is cumbersome and complex To follow is a simplified introduction to the common peripheral disorders that afflict these lengthy structures that branch and ramify throughout our bodiesIn 26 specimens, nerve staining (Sihler's staining method) and silicone rubber (Microfil) injection to the thoracodorsal artery were performed, and the relationship of the artery and the vein was examined in 10 specimens Results The thoracodorsal artery and vein always ran parallel in a deeper layer compared to the nerve The thoracodorsalA paired visceral nerve (contributes to the innervation of internal organs), carrying fibres of the autonomic nervous system (visceral efferent) as well as sensory fibres from the




Human Eye Cross Section Anatomy With All Parts Anatomical Structure Artery Vein Nerve Muscles Pupil Iris Cornea Lens Blind Spot Retina Vitreous Ciliary Body Fovea Centralis Chambers موقع تصميمي




Total Hip Replacement Doctor Stock
Most of time people get confused between the function and name of structures of our body among them the common is #ARTERIES, #VEINS & #NERVESHere is some oMnemonics to recall the order of the femoral vessels and nerve as they emerge from beneath the inguinal ligament into the femoral triangle are NAVY;And the recurrent laryngeal nerve on the right, and on the left




Difference Between Nerve And Vein Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
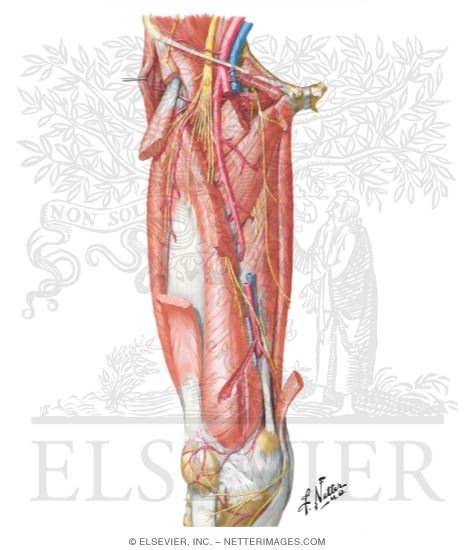



Arteries And Nerves Of Thigh Deep Dissection Anterior View Arteries And Nerves Of Thigh Anterior Views
The common carotid artery is contained in a sheath known as the carotid sheath, which is derived from the deep cervical fascia and encloses also the internal jugular vein and vagus nerve, the vein lying lateral to the artery, and the nerve between the artery and vein, on a plane posterior to both On opening the sheath, each of these threeSince arteries have to hold pressure while we're alive, they are formed with a thick tunica media which allows arteries to hold their shape Veins rely on oneway valves to get blood up to the heart, not pressure Therefore, arteries hold their thTrigeminal Neuroanatomy Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools



Viewmedica Stock Art Foot And Ankle With Arteries Veins And Nerves Skeletal Posteromedial View




Drawing To Show The Detailed Structure Of The Bowel Wall Showing The Arteries Veins Nerves Muscle Layers And Mucosal Layers Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image
Start studying Arteries, veins and nerves Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Vertebral arteries The vertebral arteries stem from the subclavian arteries; Arteries axillary, brachial, ulnar and radial arteries Veins basilic, cephalic, radial, ulnar, brachial, axillary veins Nerves branches of brachial plexus (C5T1);
/human-skull-with-veins-and-arteries--rear-view--1174640349-490cb7f8593945c4b1690b152e6a4074.jpg)



Occipital Artery Anatomy Function And Significance
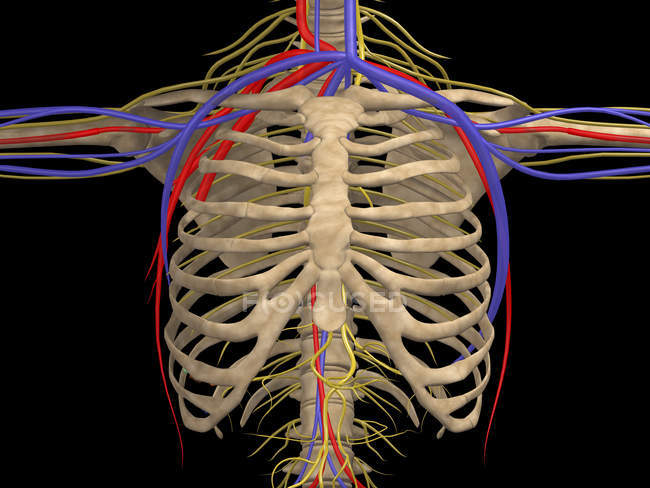



Medical Illustration Of Rib Cage With Nerves Arteries And Veins Axial Skeleton Floating Ribs Stock Photo
Start studying Anatomy arteries, veins and nerves EXAM III Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Sandwiching the occipital artery and vein is the lesser occipital nerve branch anteriorly and the greater occipital nerve branch posteriorly The lesser occipital nerve, as well as the greater occipital nerve, branches off of spinal nerve C2 just as it passes directly inferior to the first cervical vertebra, carrying fibers originating from theStart studying infra temporal fossa Arteries, Veins and Nerves;
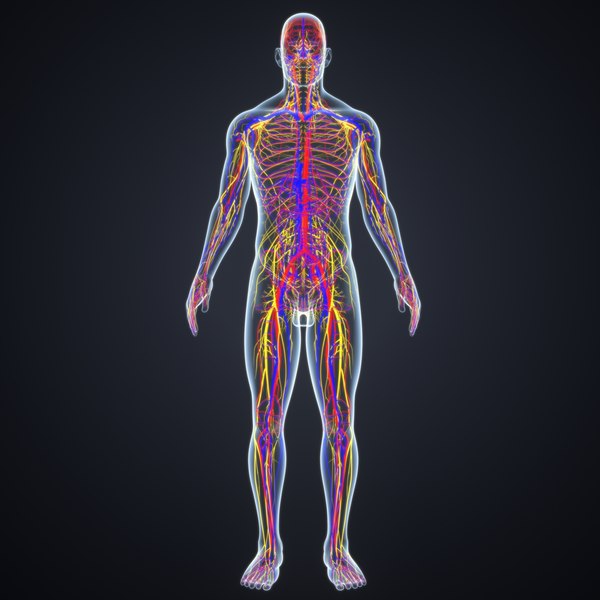



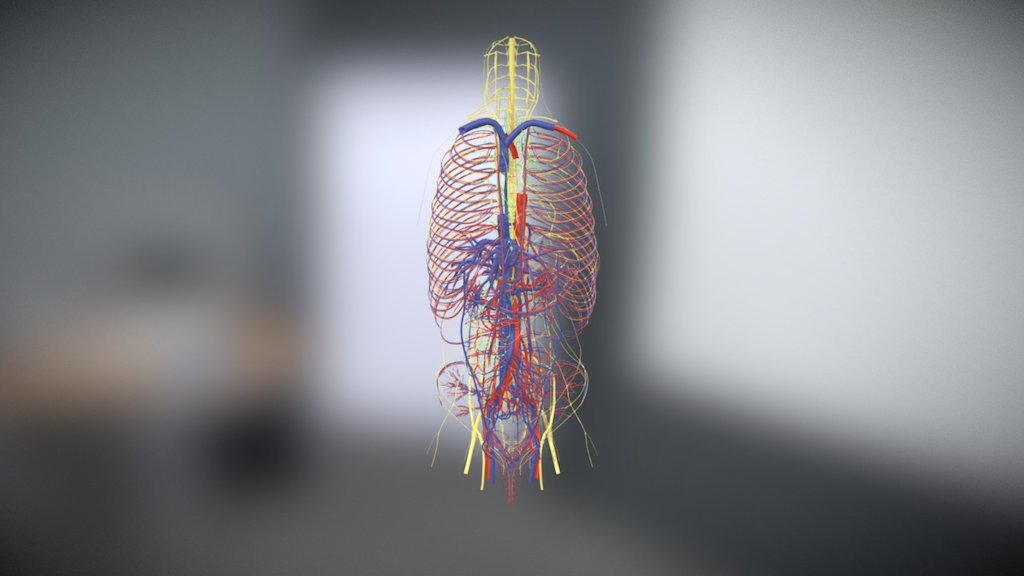
Body Arteries Veins Nerves 3d Model Turbosquid




Anatomy Of The Arteries Veins And Nerves Of The Cervical Neck Spine Region Stock Photo Alamy
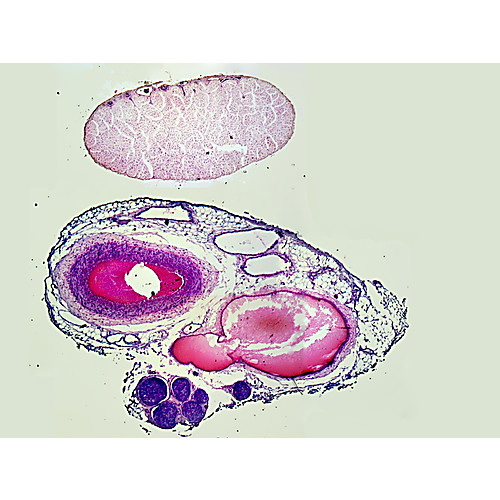
Nerve and vein are two components involved in the transportation of different elements in the animal body Nerves belong to the nervous system, but,Each artery then divides into an anterior and a posterior ramus A given posterior intercostal artery travels along the bottom of the rib with its corresponding posterior intercostal vein, as well as the intercostal nerve of the given space The vein is superior to the artery, and the intercostal nerve isArtery, Vein, nerve, lymph, kidney (histo) Nice work!




Artery Vein And Nerve Slide Flashcards Quizlet
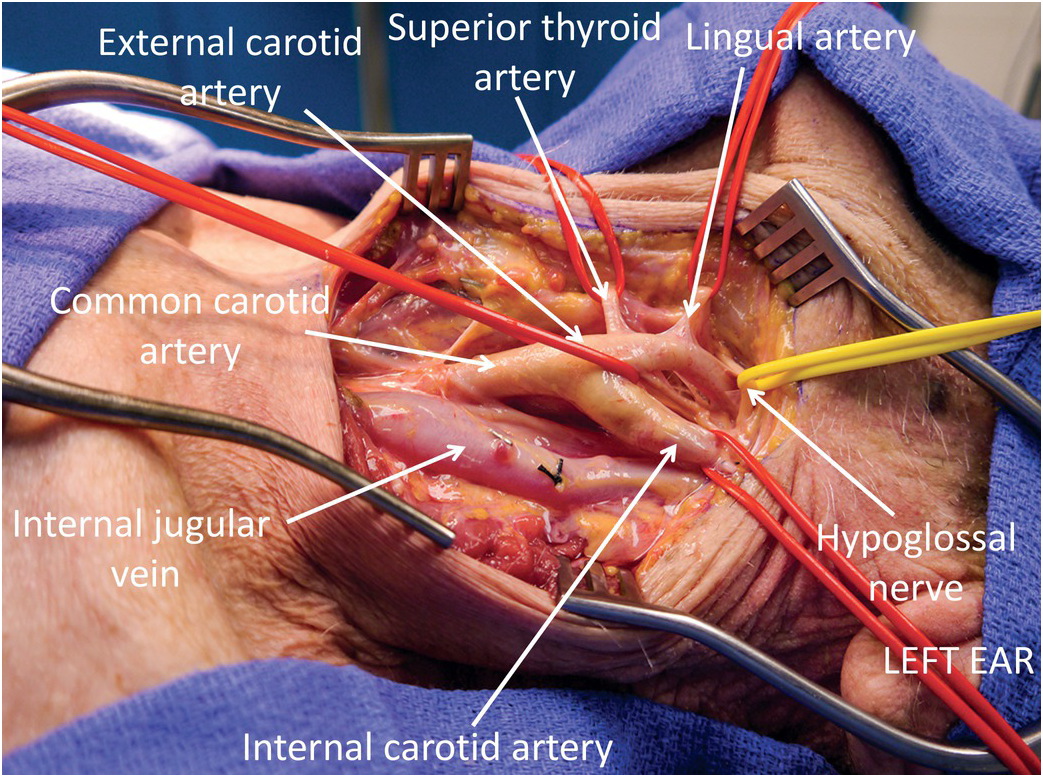



Carotid Artery And Internal Jugular Vein Injuries Chapter 8 Atlas Of Surgical Techniques In Trauma
Two major arteries of the thorax that lie beneath the claviclesThe vertebral arteries ascend through the neck inside the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae, all the way to the brainThrough their course, they give off several meningeal, muscular and spinal branches for the nearby structuresAfter a short course of about 4 cm in the thigh, the nerve is divided into anterior and posterior divisions, separated by lateral femoral circumflex artery Nerve to pectineus This nerve arises from the femoral nerve just above the inguinal ligament It passes behind the femoral sheath to reach the anterior surface of the pectineus muscleSuperior epigastric artery axillary artery lateral edge of 1st rib to inferior border of trees major muscle then continues as brachial artery
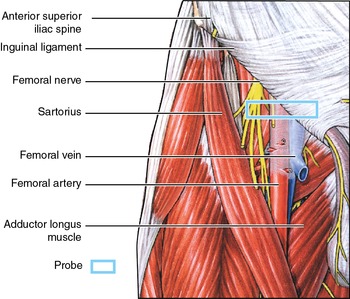



Femoral Vein Sonoanatomy For Anaesthetists



Prepared Microscope Slide Circulatory System Artery Vein Nerve
View Lab 8Concept Mappdf from BIOL 11 at University of Houston trabeculae epiphyses artery, vein, and nerve lamellae 3 tubeshaped unit perforating Veins, lymphatics and nerves of the pelvis The pelvic venous system is responsible for taking blood from the pelvic walls and viscera back to the main circulation Like the arterial analogues, the external iliac vein primarily drains the lower limbs, while the internal iliac vein drains the pelvic viscera, walls, gluteal region and perineumN Nelofer Parvin, S Dharshini, J Nithya , V Sivaranjani and V Thakini




Artery Vein And Nerve 400x Sec Petroarc International




Illustration Skin Anatomy Muscle Artery Vein Nerve Print 519
You just studied 25 terms!Neurovascular bundle what does the internal thoracic artery eventually become? Vein Veins are made up of outer tunica adventitia, middle tunica media, and inner tunica intima Function Nerve Nerves are important to carry out sensory functions Vein Veins carry deoxygenated blood towards the heart Material Transported Nerve Nerves transport electrochemical pulses Vein Veins transport deoxygenated blood Interconnection Nerve



Innervation And Arterial Supply Of The Piriformis Complete Anatomy




Human Artery Vein Nerve Cross Section Prepared Microscope Slide Eisco Labs
The popliteal artery is the continuation of the femoral artery It descends slightly lateral to the intercondylar fossa, anterior to the popliteal vein and the tibial nerve, and it ends at the inferior margin of the popliteus muscle where it divides into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries (Fig 102)Some authors use the term tibialperoneal trunk for the arterial segment Nerve (femoral nerve and femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve) Artery (femoral artery) Vein (femoral vein and it's tributary – great saphenous vein) Empty space (femoral canal) Lymph node of Cloquet/Rosenmuller and Lymphatics (within femoral canal) All are contents of the femoral sheath except the femoral nerveHere are the subclavian veins, the internal jugular veins, the brachiocephalic veins, the superior vena cava, the inferior vena cava, the azygos vein, and the hemiazygos veins Here's the phrenic nerve, and the vagus nerve, and in the chest, the vagus nerve, and the phrenic nerve;



Human Being Anatomy Blood Circulation Principal Veins And Arteries Image Visual Dictionary




Spinal Blood Supply
The phrenic nerve, pericardiacophrenic artery and vein, and the anterior pulmonary plexus, lie in front of each, and the vagus nerve and posterior pulmonary plexus lieNerves, arteries, and veins of the heart and lungs Twitter This is an excerpt from Kinetic Anatomy 4th Edition With HKPropel Access by Robert S Behnke,Jennifer L Plant & Jennifer L Plant The two major organs housed within the thorax are the heart and lungs As with all other anatomical structures, the heart and lungs need nerves and bloodVascular Supply of the Kidney Renal Artery, Vein and Nerves Renal Artery The kidneys are supplied by parietal branches of the aorta (renal artery) The vascular supply (A renalis dexter et sinistra) is often subject to variations The right renal artery passes under the




Rectal Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Untitled Document
This artery runs underneath the optic nerve and lies within the dural sheath of the nerve to reach the eyeball It pierces the optic nerve itself near the back of the eye, and sends numerous branches over the internal aspect of the retina




Hip And Thigh Arteries Veins And Nerves Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11147/upper-arm-nerves-vessels_english.jpg)



Major Arteries Veins And Nerves Of The Body Anatomy Kenhub
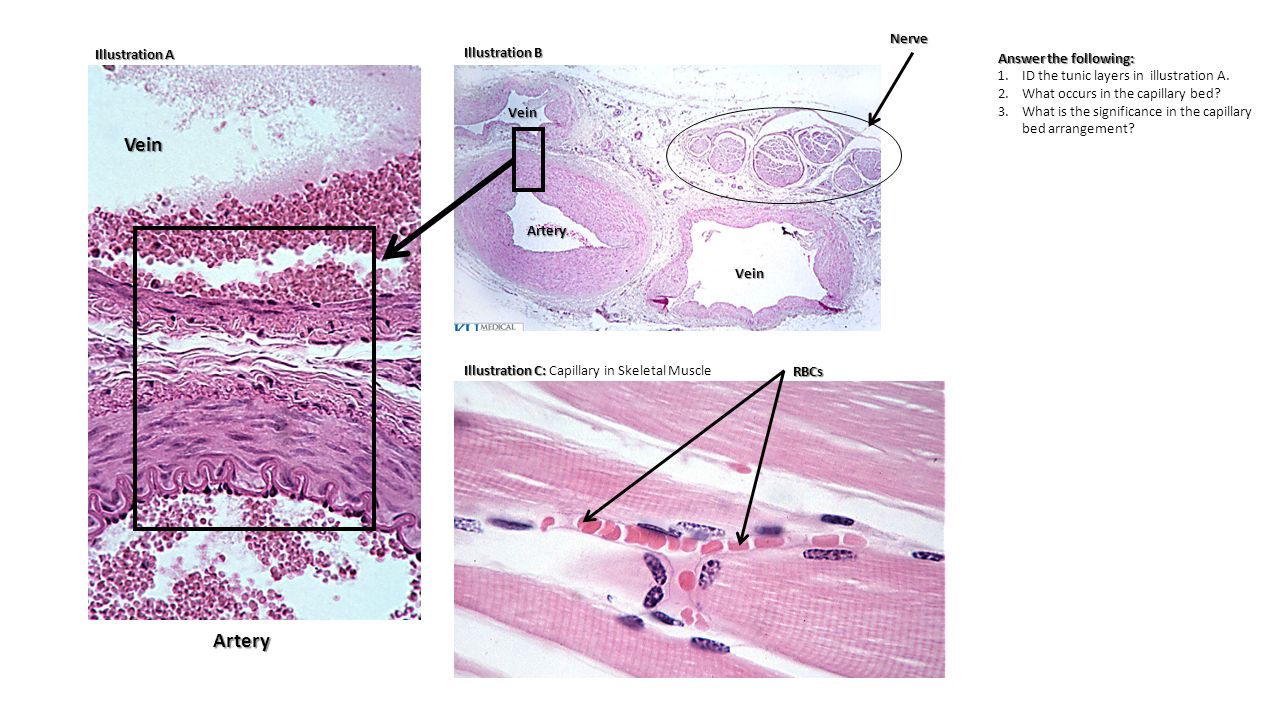



Tunica Tunica Artery Vein Capillary Ppt Download
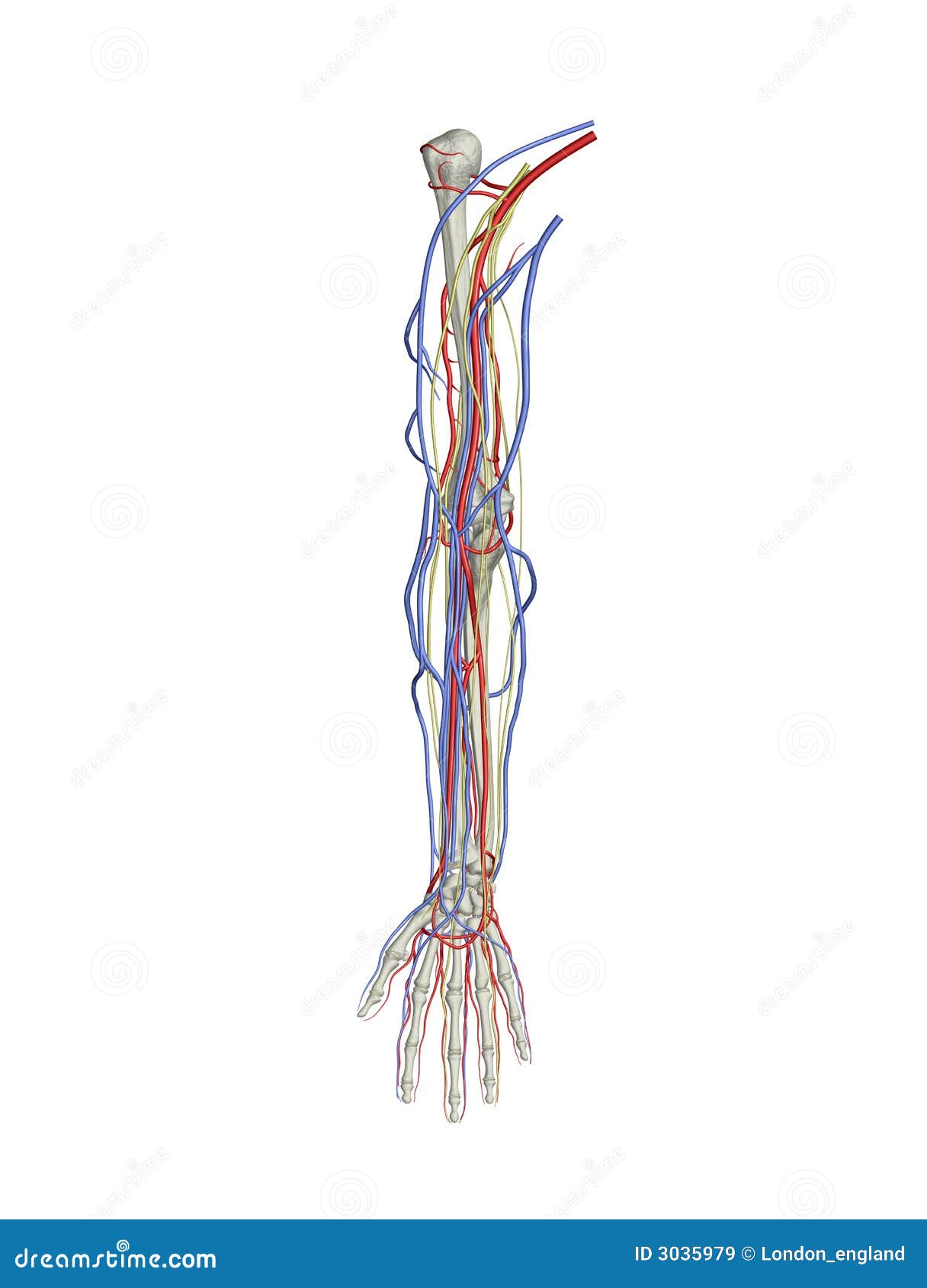



Arm Arteries Veins Nerves Stock Illustration Illustration Of Medicine



Arm Arteries Veins Nerves Stock Illustration Illustration Of Medicine




Medivisuals Resection And Transection Of The Principle Artery Vein And Nerves To The Arm Medical Illustration



Arteries Veins Nerves And Lymphatics 3d Model By Kfiebke Kfiebke B5dbe00




Illustration Of The Femoral Nerve Block Region Showing The Femoral Download Scientific Diagram



Veins And Arteries Petroarc International




Muscular Artery And Nerves Light Micrograph Stock Image C036 1276 Science Photo Library



Block3 Fig 11 93w4046 Artery Vein Nerve Elastic Tissue Cs V E



1




ɹǝʇlnoԁ Piʌɐᗡ 𝔹𝕖 𝕜𝕚𝕟𝕕 En Twitter Fascinating Fact The Transvers Process Of The Cervical Spine Is Placed Anterior And Acts As A Protective Gutter For The Exiting Nerve It
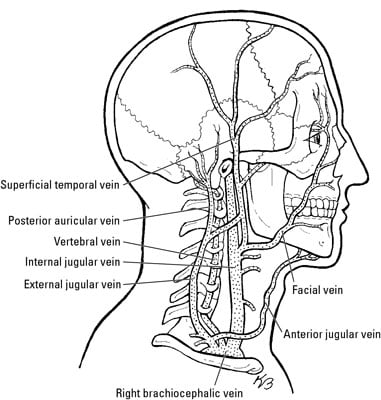



Nerves And Blood Vessels In The Root Of The Neck Dummies




Femoral Artery Vein Nerve Anatomy




Head And Neck Anatomy Common Carotid Artery Vein Superficial Temporal Nerve Face Hand Png Pngegg
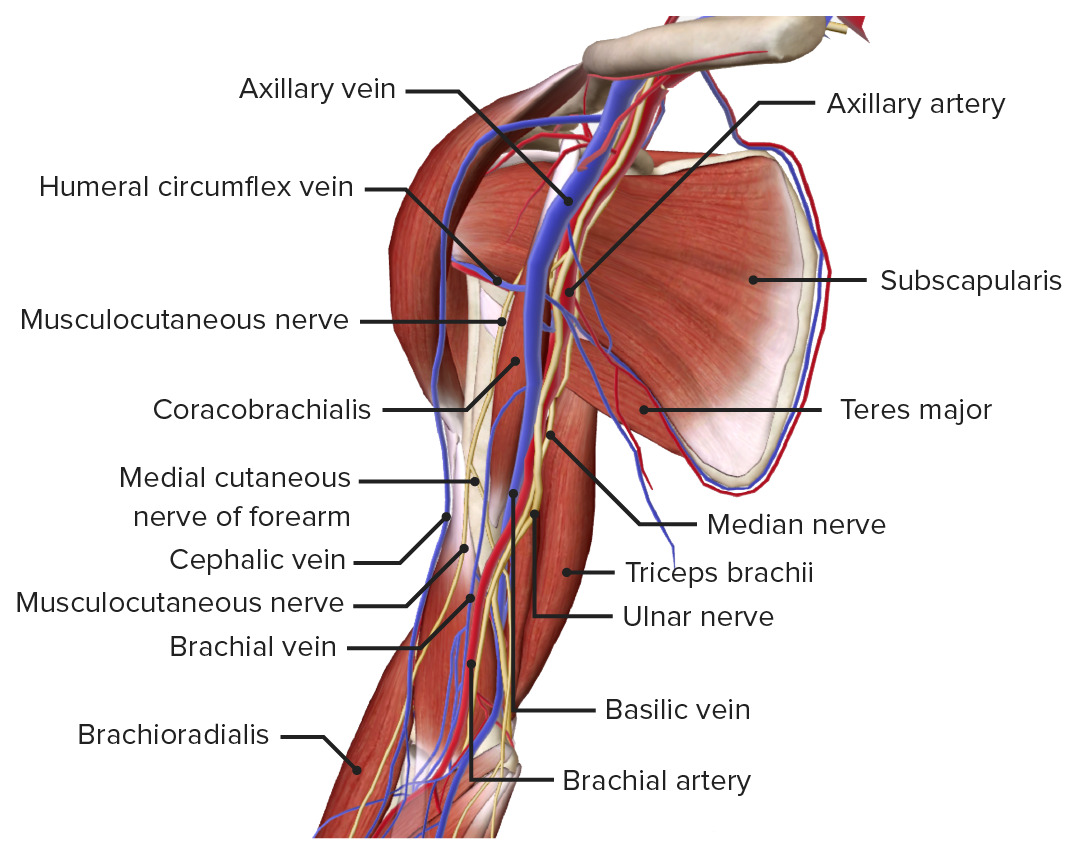



Arm Anatomy Video Lecturio Medical
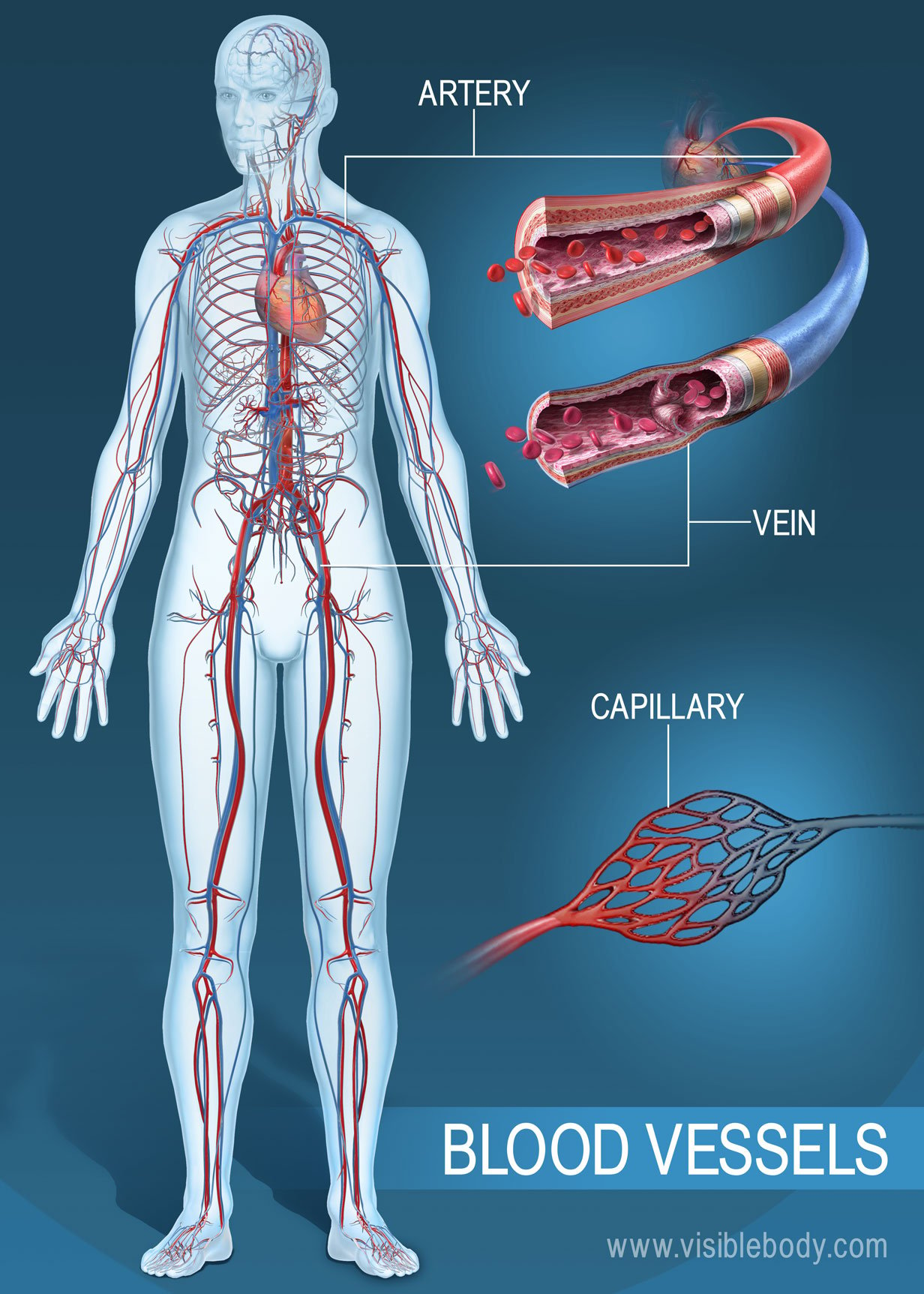



Blood Vessels Circulatory Anatomy
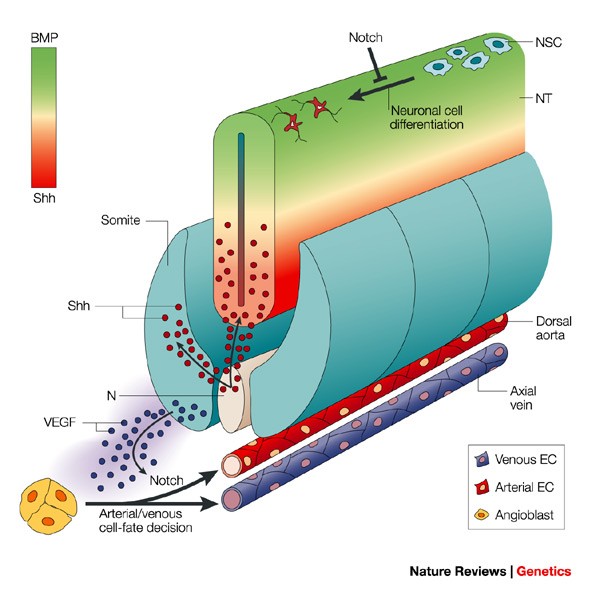



Blood Vessels And Nerves Common Signals Pathways And Diseases Nature Reviews Genetics



Viewmedica Stock Art Foot With Arteries Veins And Nerves Skeletal Dorsal View Facing Down




Major Arteries Veins And Nerves Of The Arm Trialexhibits Inc
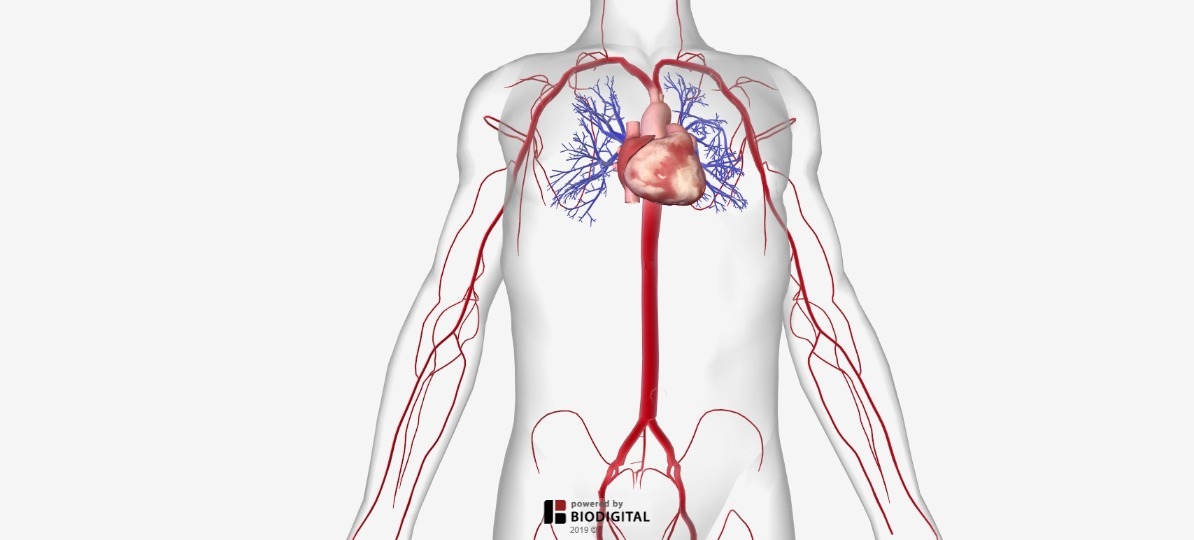



Arteries Of The Body Picture Anatomy Definition More
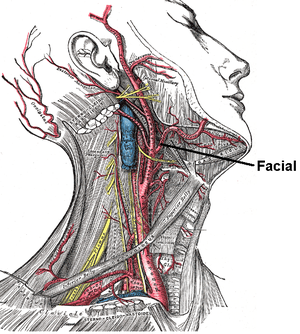



Facial Artery Wikipedia




Arteries Veins Nerves Image Photo Free Trial Bigstock
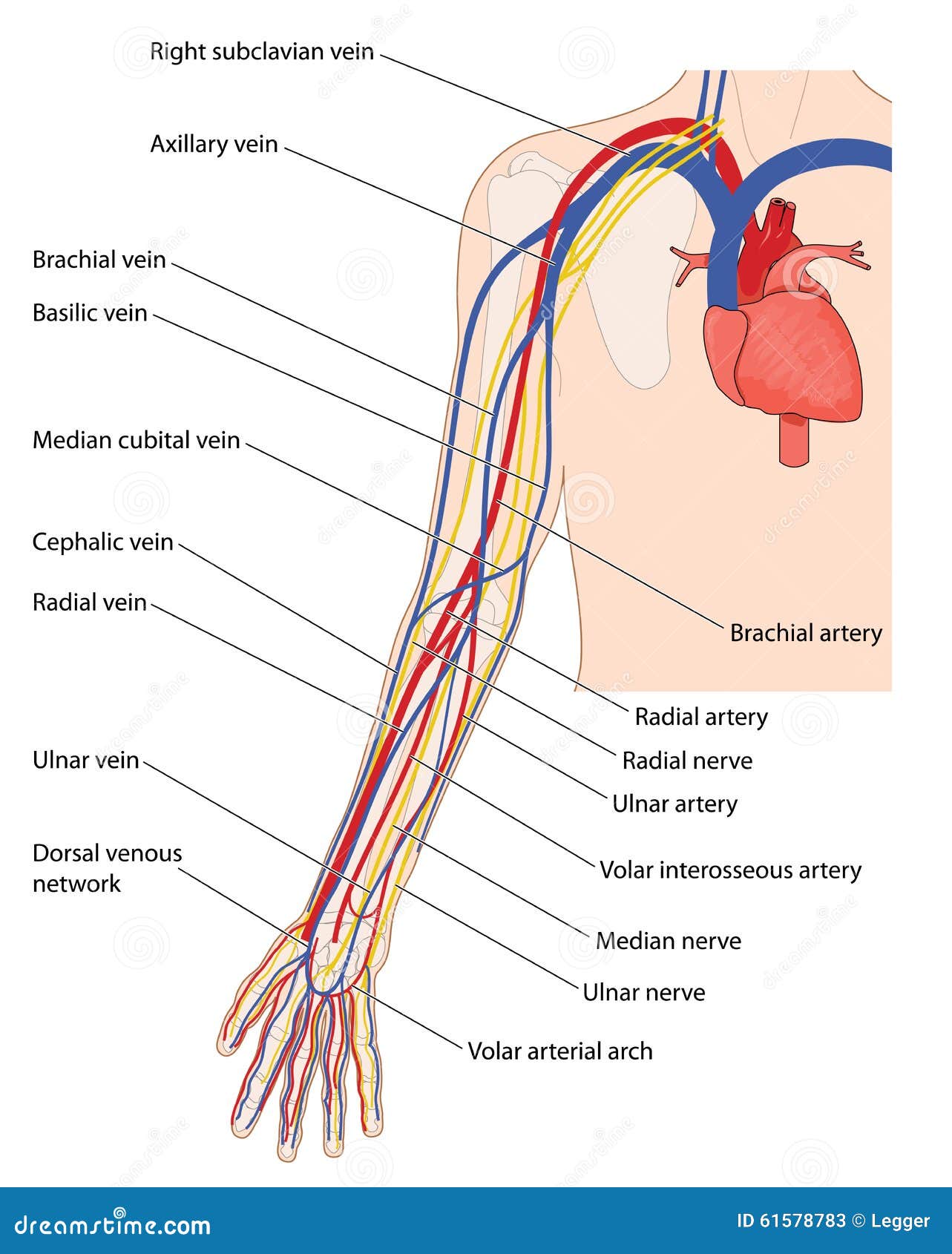



Blood Vessels And Nerves Of The Arm Stock Vector Illustration Of Cubital Interosseous




Carotid Artery Disease Symptoms Treatment Life Expectancy Causes



How Does A Nerve Artery And Vein Feel On Touching Quora




Anatomy Bony Pelvis And Lower Limb Saphenous Nerve Artery And Vein Article




Arteries Veins Nerves Image Photo Free Trial Bigstock




Causes Of Tos Compression Of Artery Vein Or Nerves In The Thoracic Outlet




Arteries Veins Neck Human Body Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology Arteries And Veins




Artery And Vein Stock Image Image Of Tissue Nerve



Arteries Of The Body Picture Anatomy Definition More
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11144/pasted_image_0__1_.png)



Major Arteries Veins And Nerves Of The Body Anatomy Kenhub




Artery And Vein




What Is The Difference Between Arteries Veins Nerves Youtube
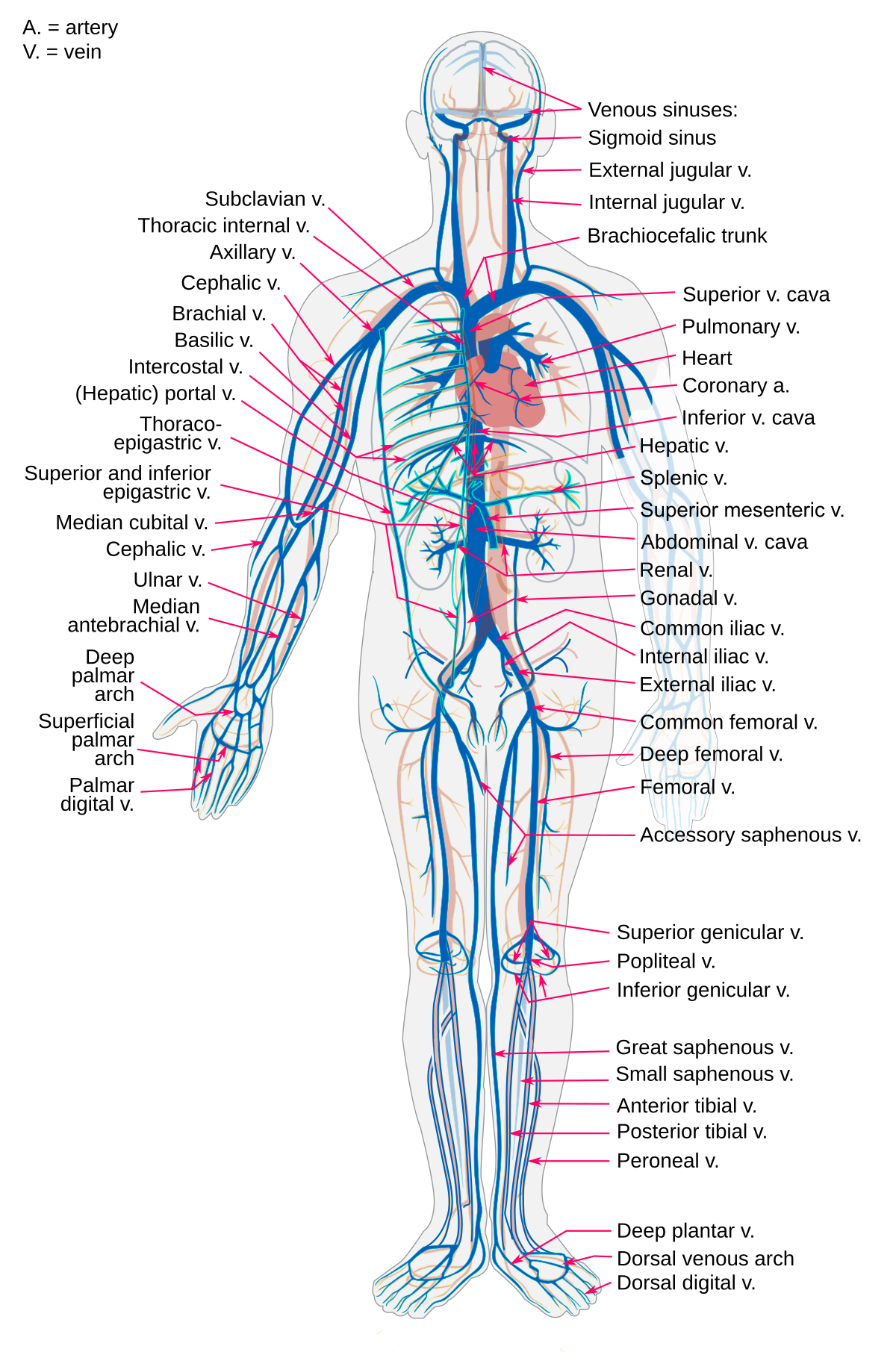



Vein Wikipedia




Pectoral Arteries Veins And Nerves
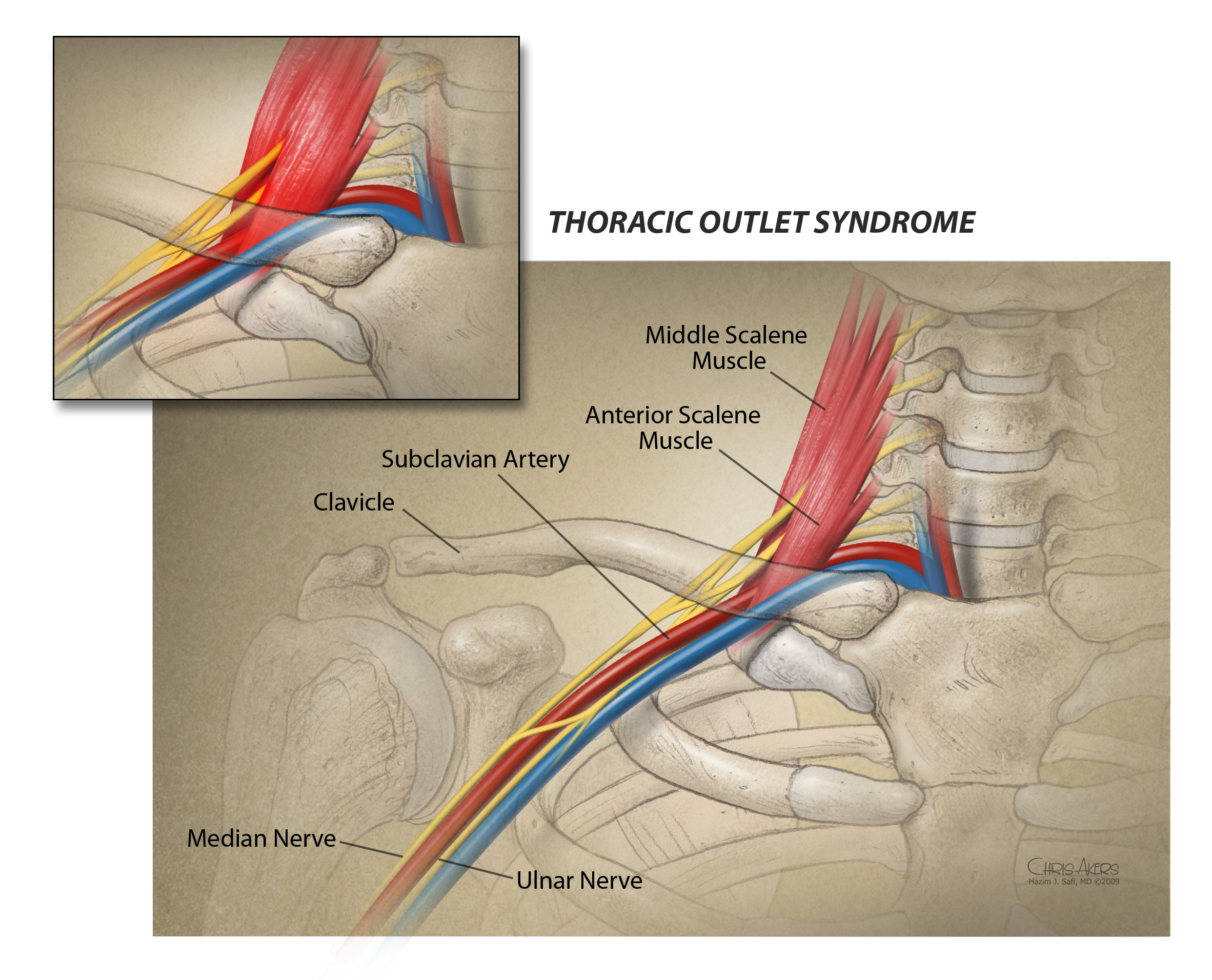



Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Tos Mcgovern Medical School
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11148/nerves-vessels-pelvis-thigh_english.jpg)



Major Arteries Veins And Nerves Of The Body Anatomy Kenhub




Intercostal Veins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Untitled Document




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
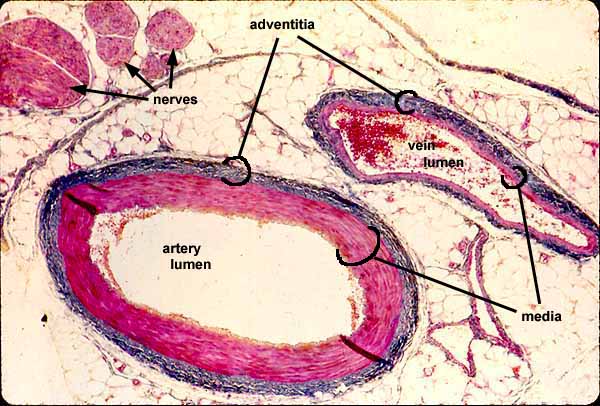



Histology At Siu




Pin On Learning




Figure Arteries And The Veins Of Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
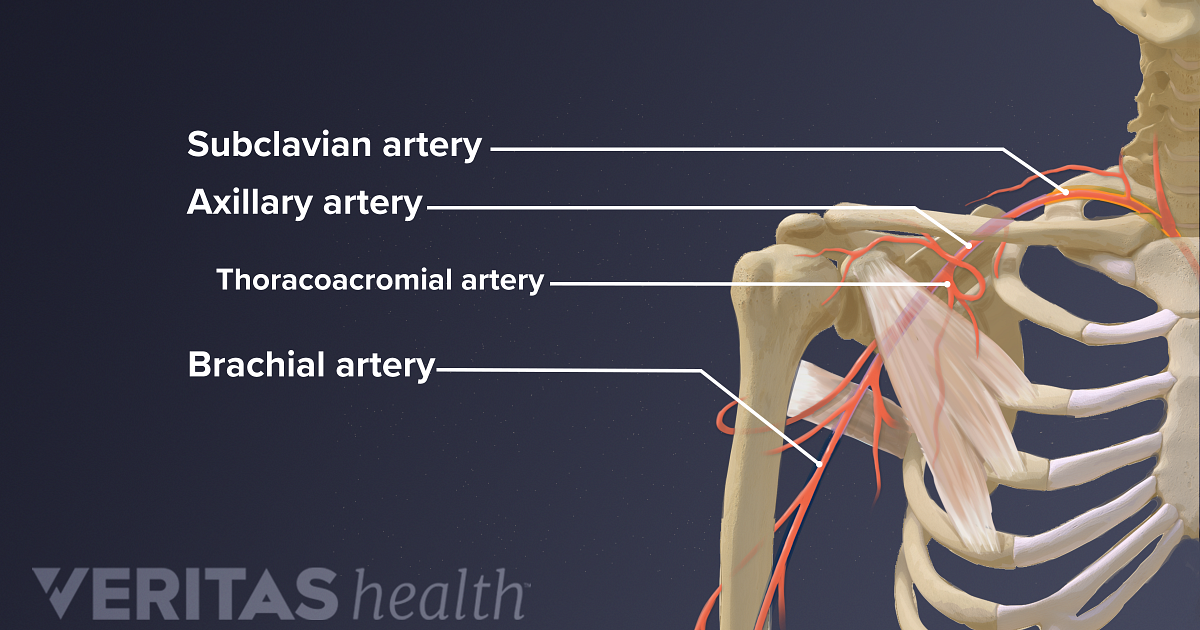



Blood And Nerve Supply Of The Shoulder
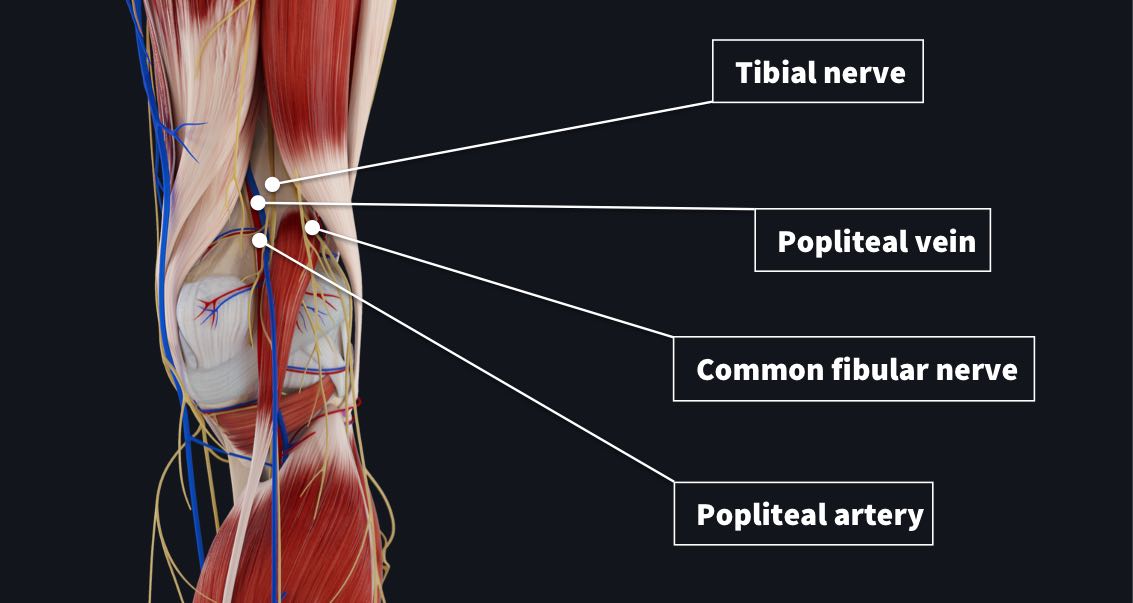



The Popliteal Fossa Complete Anatomy




Blood Supply To Hand Hand Orthobullets



Http Ksumsc Com Download Center Archive 1st 436 2 musculoskeletal block Team work Anatomy 13 Vascular of upper limb Pdf
/GettyImages-87302280-83604c7a3ca84315a84304a002377404.jpg)



Femoral Vein Anatomy Function And Significance




Arteries Or Veins What S The Difference
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10691/7AKXp7rxwNtNBH7cVd2NPQ_5wsNg7baK5_Arteria_axillaris_2.png)



Upper Limb Arteries Veins And Nerves Kenhub




Body Arteries Veins Nerves Lymph Nodes Stock Illustration




Neurovasculature Of The Lower Limbs Knowledge Amboss




Circulatory Np Histology



1




Anterior Thigh




Artery Vein Nerves Of Orbit Diagram Quizlet




Anatomy Of The Nerves Arteries And Veins Of The Arm Upper Extremity Labels Include Cephalic Vein Brachial Ar Nerve Anatomy Arteries And Veins Median Nerve



1




Upper Extremity Anatomy Arteries Veins Muscles Free Pdf Epub Medical Books




Anatomy Of The Femoral Nerve Artery And Vein Medical Illustration




Exercise 21 Blood Vessels Circulation Portland Community College




Artery Vein Nerve Histology Diagram Quizlet




A Unique Variation Of The Inter Relationship Between The Internal Iliac Download Scientific Diagram



Navel Nerve Artery Vein Empty Space And Lymphatic By Acronymsandslang Com
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12652/Introduction.png)



Nerves And Arteries Of Head And Neck Anatomy Branches Kenhub




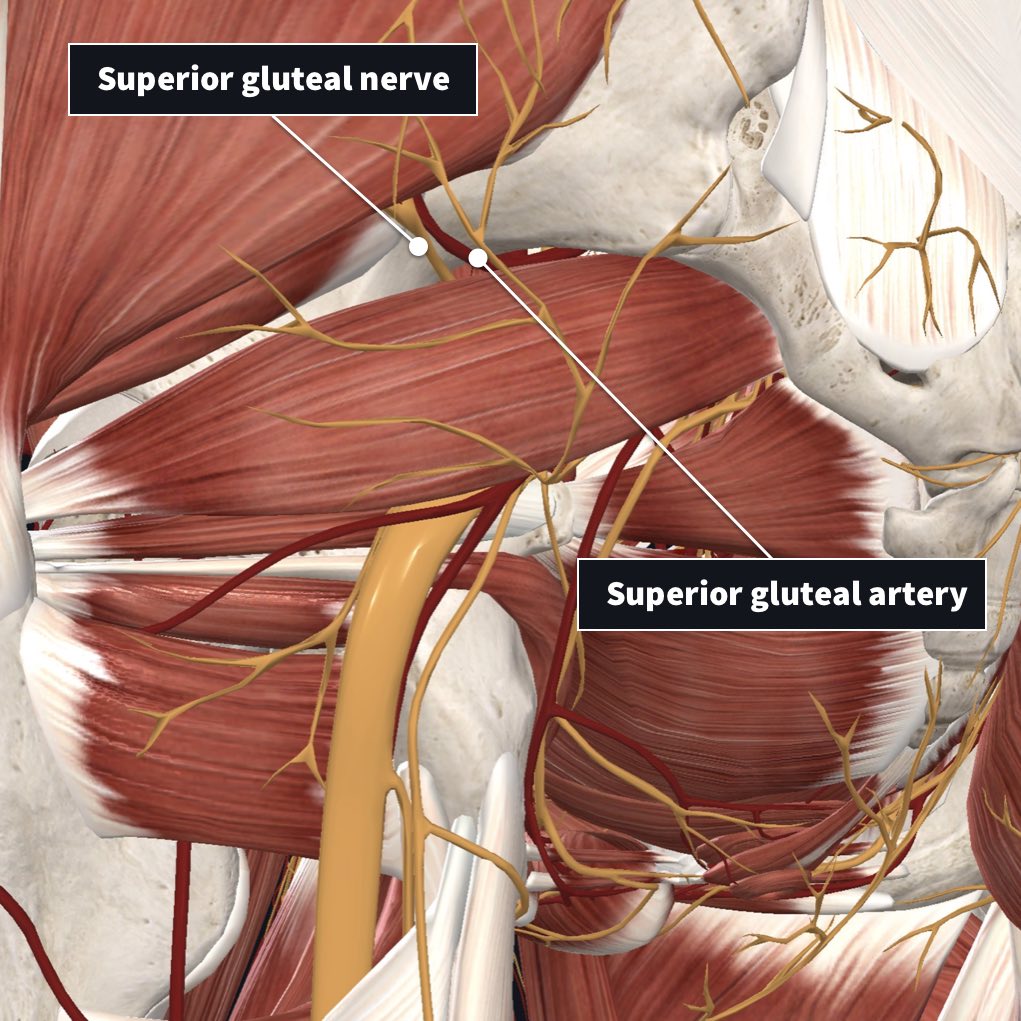
Superior Gluteal Veins Wikipedia



Description
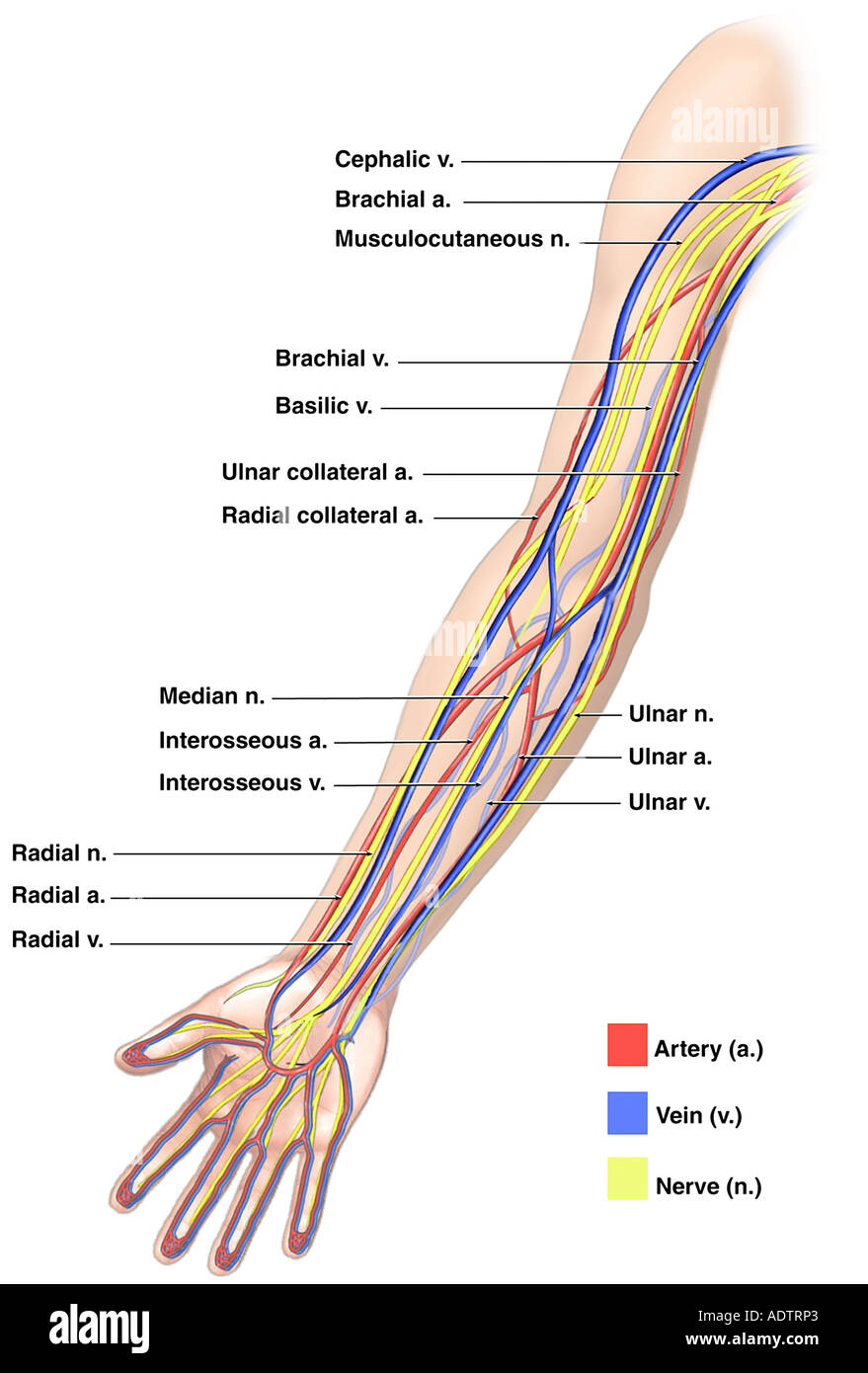



Anatomy Of The Nerves Arteries And Veins Of The Arm Upper Extremity Stock Photo Alamy




Knee Joint Muscle Anatomy Arteries Veins Stock Illustration



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿